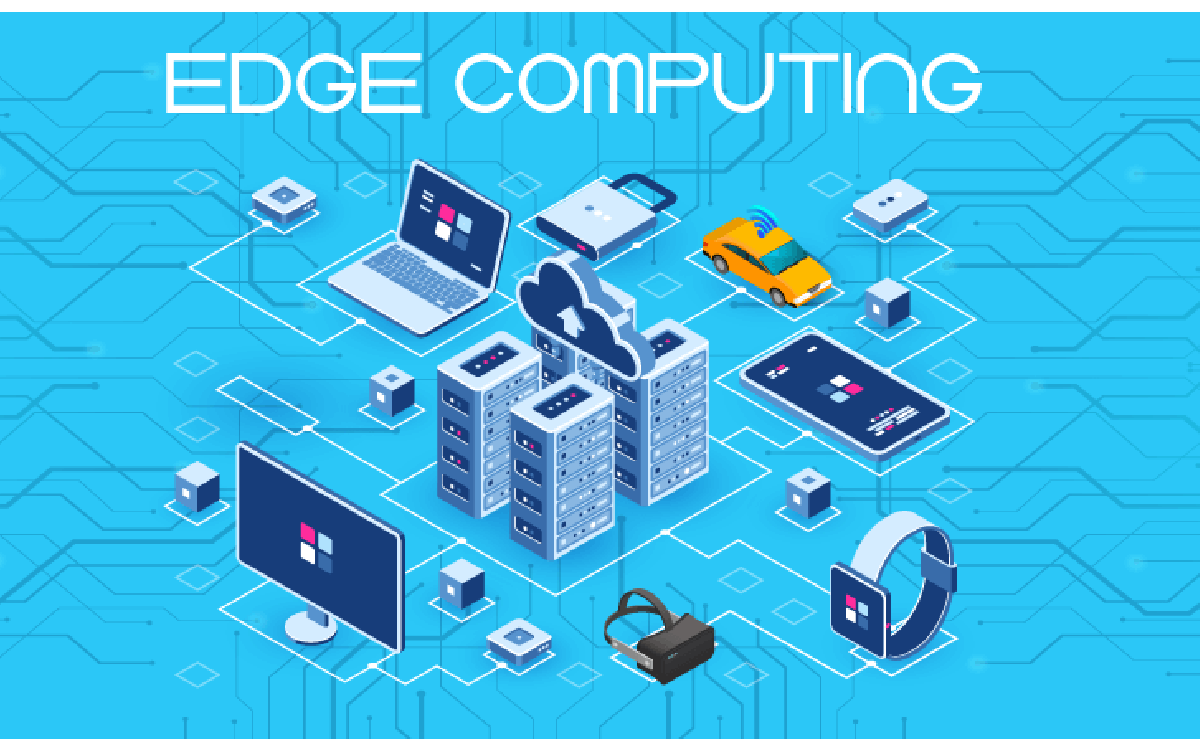
Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that brings computation and data storage closer to the devices where data is generated and consumed. This is in contrast to traditional cloud computing, which centralizes computation and data storage in large data centers.
Edge computing has a number of advantages over cloud computing, including:
- Reduced latency: Edge computing can reduce latency by processing data locally, rather than sending it back and forth to a central data center. This is important for applications that require real-time responses, such as self-driving cars and augmented reality.
- Improved bandwidth efficiency: Edge computing can improve bandwidth efficiency by reducing the amount of data that needs to be sent over the network. This is important for applications that generate a lot of data, such as video streaming and industrial IoT.
- Reduced costs: Edge computing can reduce costs by reducing the amount of cloud computing resources that are needed. This is important for businesses that are looking to optimize their IT costs.
Edge computing is still in its early stages of development, but it is rapidly gaining traction in a wide range of industries, including:
- Transportation: Edge computing is being used to power self-driving cars, traffic management systems, and other transportation applications.
- Manufacturing: Edge computing is being used to improve the efficiency and productivity of manufacturing processes.
- Retail: Edge computing is being used to power personalized shopping experiences, inventory management systems, and other retail applications.
- Healthcare: Edge computing is being used to power wearable devices, real-time patient monitoring systems, and other healthcare applications.
- Security: Edge computing is being used to power security cameras, intrusion detection systems, and other security applications.
Here are some examples of how edge computing is being used in the real world:
- Self-driving cars: Self-driving cars need to be able to make decisions in real time, which means that they can’t afford to send data back and forth to the cloud for processing. Edge computing allows self-driving cars to process data locally, which reduces latency and improves safety.
- Smart cities: Smart cities use a variety of sensors to collect data about everything from traffic to air quality. Edge computing can be used to process this data in real time and provide insights that can be used to improve the efficiency and livability of cities.
- Industrial IoT: The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is transforming the manufacturing industry by connecting machines and devices to the internet. Edge computing can be used to improve the efficiency and productivity of IIoT systems by allowing them to process data locally.
- Wearable devices: Wearable devices, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, generate a lot of data. Edge computing can be used to process this data locally and provide real-time insights to users.
Edge computing is a rapidly evolving field with a wide range of potential applications. As edge computing technologies continue to mature, we can expect to see even more innovative and transformative uses for edge computing in the future.